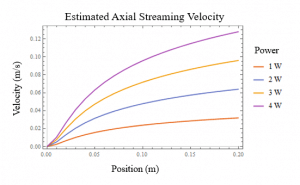
Acoustic streaming is a complicated phenomenon, with many different numerical methods proposed to describe flow patterns caused by an ultrasonic source. In the development of the control system for this project, it was desired to compare more sophisticated and computationally expensive finite-element calculations with simplified models to identify key parameters a real-time control system should focus on. This plot shows the results of the simplified equations developed by Nowicki et al. [1] applied to the conditions of Botton et al. [2] in their experimental and numerical work. Strong agreement in velocity profile was found, allowing analysis to continue into the estimation of acoustic power output from transducers based on electrical power input.
[1] Nowicki et al., Estimation of acoustical streaming: theoretical model, Doppler measurements and optical visualisation, European Journal of Ultrasound, (1998), 73-81.
[2] Botton, Valéry et al, Near-field acoustic streaming jet, American Physical Society, 91 (2015) 3.
Students involved in this project:
Mark McDermott
Bryson Rogers
Marco Kleimans
Yifan Xue