The information on this page was prepared by:
| Joseph Ruhl | jruhl@usc.edu | Computer Engineering and Computer Science |
| TianLi Woon | twoon@usc.edu | Electrical Engineering |
Coal: Introduction
Coal is a combustible mineral formed from the remains of trees, ferns and other plants that existed and died during the time of the dinosaurs. It generates more than half the electricity used in the United States and is far more plentiful than domestic oil or natural gas, accounting for some 95 percent of the nation’s fossil energy reserves.
The United States has nearly 275 billion tons of recoverable coal which is more than 250 years of supply at today’s usage rates. Nine of every 10 tons of coal used in the United States are for electricity generation. It is by far the cheapest source of power fuel per million Btu, averaging less than half the price of petroleum and natural gas.
Though coal is one of the most polluting fuels for power generation, much is being done to reduce harmful emissions from the combustion of coal. While coal use for domestic electricity has more than tripled since 1970, government statistics show sulfur dioxide emissions have decreased more than 35 percent below 1970 levels.
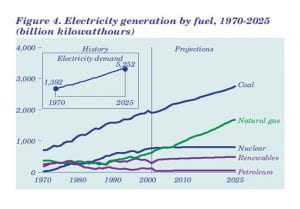
http://www.eia.doe.gov/oiaf/aeo/figure_4.html
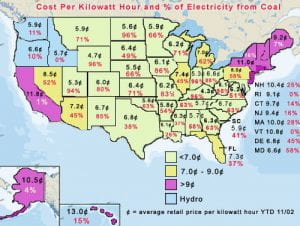
Coal Use and the Cost of Electricity in the U.S.
This map provides the cost of electricity in every state (average retail price per kilowatt hour YTD 11/02) and the percent of total generation from coal for 2001.