The information on this page was prepared by:
| Daniel Marsh | marshd@usc.edu | Computer Science |
| Nick Firdaus Mohd Husin | mohdhusi@usc.edu | Electrical Engineering |
Introduction
Alkali Fuel Cells (AFC) set the precedent for other fuel cells in their design and application. This fuel cell boasts an efficiency of 70% and has been used by NASA in space shuttle missions. Due to the use of potassium hydroxide as the electrolyte, Alkali fuel cell have a wide temperature range: freezing below -40C and controlled at 70C for maximum power.
How It Works
The fuel cell uses a potassium hydroxide electrolyte that flow through the center of two porous membrane fuel plates, one with a platinum catalyst and the other with a silver catalyst. Hydrogen is used as the anode and flows through the platinum side, while oxygen is used as the cathode and flows through the silver side.
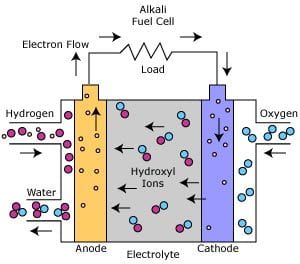 http://www.fctec.com/fctec_types_afc.asp
http://www.fctec.com/fctec_types_afc.asp
The Alkali fuels cells create power by having hydroxyl ions flow from the cathode to the anode. A reaction between the hydrogen and hydroxyl ions takes place and forms water vapor and releases electrons. The water vapor is then returned to the electrolyte tank to sustain water equilibrium. The release of electrons during the reaction of hydrogen and hydroxyl ions is the basics for creating power in an Alkaline Fuel Cell. After their release, the electrons create electric power to an external circuit. After they are used they are returned to the cathode and start they cycle over, by reacting with oxygen to produce hydroxyl ions that will soon move to the anode.
Application
In the 1960’s NASA developed alkali fuel cells for use in space. NASA chose the alkali fuel cells for many reasons including their ability to work in wide range of temperatures, the 70% power generating efficiency, and the drinking water that is produced by the chemical reaction. Recently many companies have been researching how to reduce the cost and the versatility of the expensive Alkaline Fuel Cell. One of the most successful companies has been the Zero Emission Vehicle Company (ZEVCO) located in England ; ZEVCO introduced a prototype taxi in July 1998. ZEVCO reduced the cost of the fuel cell installed in their product by using cobalt instead of platinum. The ZEVCO vehicles not only produce less air pollution but also reduce noise pollution greatly.
http://fuelcells/si.edu/alk/alkmain.html
