The information on this page was prepared by:
| Mohd Suffian Muhili | mohdmuhi@usc.edu | Electrical Engineering |
Wind Energy: Technology
A wind turbine converts the force of the wind into a torque (turning force) that turns the turbine blades, which are connected to the shaft of an electric generator. The amount of energy that the wind transfers to the blades depends on the density of the air, the blade area, and the wind speed. On the other hand, wind speed determines how much energy is available for electricity production.
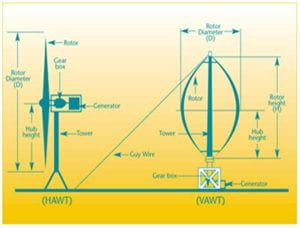
There are a lot of components in a wind turbine but six are considered as the major components: They are: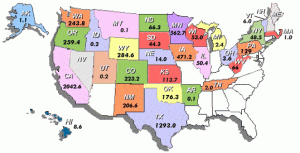
Wind Energy Projects throughout the United States of America
As of January 21, 2004
| Turbine Components | Function |
| Nacelle | Contains the key components of the wind turbine, which includes including the gearbox and the electrical generator |
| Rotor | Aerodynamically converts the wind energy into mechanical energy on a slowly turning shaft |
| Gearbox | Increases the rotor-shaft speed for the generator that later, produces electricity |
| Control and Protection System (Electronic Controller) | Optimizes performance and keeps the operation of the machines within the safe limits |
| Tower | Raises the rotor high off the ground where the wind speed is greater and the effects of local obstructions are less |
| Foundation | Supports the wind turbine system |